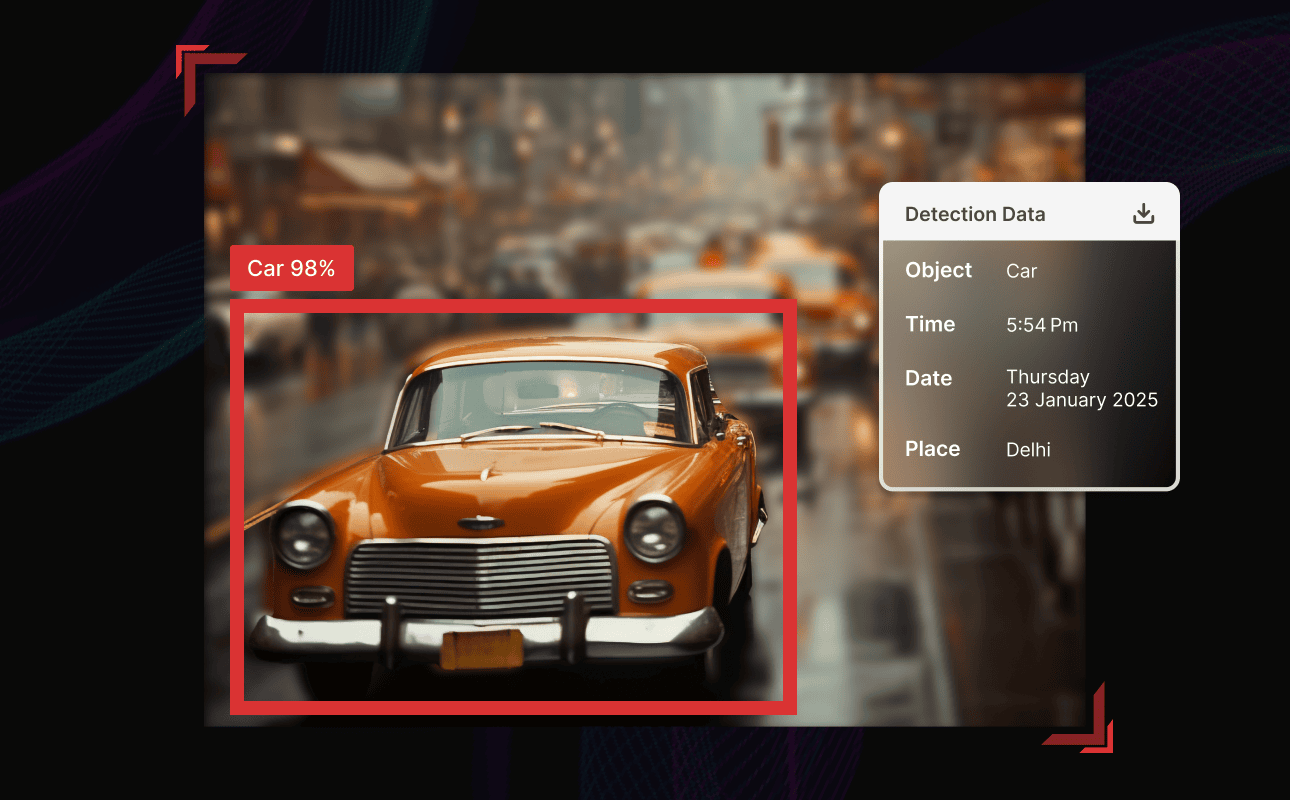
Attempt to inform a child about the difference between an apple and an orange and never expose them to actual examples. Attempt to paint a picture with them about their colors, shapes, and textures, but until such a point when they can actually see and touch both fruits, they will have difficulty distinguishing between them. AI behaves in a similar way. For AI to “see,” “hear,” and “know” about the world, it must have duly labeled information to learn from. That is when data annotation comes in.
In today’s AI-driven world, properly labeled data powers everything from self-driving cars recognizing pedestrians to chatbots understanding our questions. High-quality annotated data acts as AI’s teacher, making sure it learns accurately and makes reliable decisions.
Being a top AI & ML development company, we can firmly say that without data annotation, AI would be like a child left guessing about apples and oranges—stumbling through the world without knowing what’s what.